The NINDS Translational Biomarker Program
The NINDS Biomarker Program is focused on improving the quality and efficiency of neurotherapeutic clinical research by supporting rigorous biomarker development and validation. In order to achieve this goal, the program: 1) promotes rigorous biomarker identification and validation through milestone-driven funding opportunities, and 2) facilitates the validation of biomarkers and biomarker signatures as fit for purpose tools for use in clinical trials to accelerate therapeutic development and aid in decision making for patient care. A biomarker is a defined characteristic that is used as an indicator of normal biological processes, pathogenic processes or responses to a therapeutic intervention.
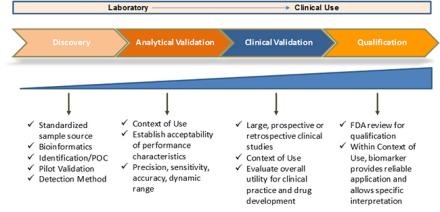
Biomarkers are recognized as essential tools for the development of therapeutics, allowing improved and better informed clinical trial design through indicators of target engagement and those that enable patient stratification. In addition, biomarkers can facilitate the evaluation of therapeutic intervention on disease progression or recurrence. Although biomarker discovery is a very active research area, few biomarkers have been sufficiently validated for use in clinical practice or clinical trials.
NINDS Biomarker Funding Opportunities
Translational Funding Opportunities
- Digital Biomarkers
- Biomarker Development
- Analytical Validation
- Clinical Validation
Other Funding Opportunities
Related Resources
Funded Projects and Publications
NINDS Funded Biomarker Projects and Publications
List of all current (active) NINDS supported projects available in the NIH RePORTER database, with associated publications.
HEAL Funded Biomarker Projects and Publications
List of all current (active) HEAL supported projects available in the NIH RePORTER database, with associated publications.
News & Events
| Event Title | Date(s) |
|---|---|
| NINDS Biomarker Program: Digital Health Technology Derived Biomarker Webinar Webinar Slides(pdf, 2523 KB) | December 11, 2024 |
| NINDS Biomarker Webinar | January 11, 2024 |
| NINDS Advancing Digital Endpoints and Digital Health Technologies for Neurological and Neuromuscular Disorders Workshop | September 18, 2023 September 29, 2023 October 10, 2023 |
| OPEN Stage webinar - Biomarker development and validation: Translating discoveries into fit-for-purpose clinical tools | January 30, 2023 |
| NIH Workshop: Discovery and Validation of Biomarkers to Develop Non-Addictive Therapeutics for Pain | November 14-15, 2018 |
| Researchers examine how Parkinson's disease alters brain activity over time | August 15, 2016 |
Proceedings & Outcomes
Related Federal Programs
Foundation for the National Institutes of Health Biomarkers Consortium
Brings together diverse partners around a common mission to develop promising biomarkers in order to help accelerate the delivery of successful new technologies, medicines and therapies for prevention, early detection, diagnosis and treatment of disease.
FDA Biomarker Qualification Program
The CDER Biomarker Qualification Program (BQP) works with external stakeholders to develop biomarkers as drug development tools. Qualified biomarkers have the potential to advance public health by encouraging efficiencies and innovation in drug development.
Resources
The Accelerating Medicines Partnership (AMP) is a public-private partnership between the National Institutes of Health (NIH), multiple biopharmaceutical and life sciences companies, and non-profit organizations. The research plan proposed for AMP PD encompasses a deep molecular characterization and longitudinal clinical profiling of PD patient data and biosamples with the goal of identifying and validating diagnostic, prognostic and/or disease progression biomarkers for Parkinson’s disease (PD). AMP PD utilizes well characterized cohorts with existing biosamples and clinical data that were collected under comparable protocols and using common data elements.
Clarifies terminology and uses of biomarkers and endpoints as they pertain to the progression from basic biomedical research to medical product development to clinical care. Developed by FDA and NIH to promote consistent use of biomarker terms and concepts, and thereby advance biomarker science.
Extensible, scalable informatics platform for traumatic brain injury (TBI) relevant data (medical imaging, clinical assessment, environmental and behavioral history, etc.) and for all data types (text, numeric, image, time series, etc.). FITBIR was developed to share data across the entire TBI research field and to facilitate collaboration between laboratories, as well as interconnectivity with other informatics platforms.
Provides draft guidance to industry on enrichment strategies that can be used in clinical trials intended to support effectiveness and safety claims in new drug applications (NDAs) and biologics license applications (BLAs).
NIH NeuroBioBank
Banks and distributes human post-mortem brain tissue and related biospecimens that span neurological, neuropsychiatric, and neurodevelopmental diseases and disorders. The NBB serves as a central point of access to the world-class collections of six biorepositories. In addition, the NBB provides researchers with a wealth of resources to facilitate their research, including medical records and clinical data sets (when available) as well as access to quality metrics and best practices used by each site.
Banks and distributes biological samples that can be used to identify biomarkers of disease susceptibility, onset and progression for neurological and neuropsychiatric diseases. BioSEND currently banks biospecimens, including DNA, plasma, serum, RNA, CSF, and saliva.
An iPSC-based biorepository with cell sources that include fibroblasts and/or induced pluripotent stem cells for Alzheimer’s Disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Ataxia-telangiectasia, Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration (FTD), Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and healthy controls. Cell sources, including isogenic cell lines for current and new diseases covered by the NINDS are continuing to be added.
