Scientists find responses to mixed odors are more complex than previously thought
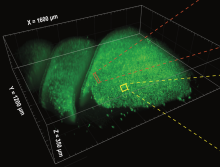
Our ability to study networks within the nervous system has been limited by the tools available to observe large volumes of cells at once. An ultra-fast, 3D imaging technique called SCAPE microscopy, developed through the National Institutes of Health (NIH)’s Brain Research through Advancing Innovative Technologies (BRAIN) Initiative, allows a greater volume of tissue to be viewed in a way that is much less damaging to delicate networks of living cells.
In a study published in Science, researchers used SCAPE to watch for the first time how the mouse olfactory epithelium—the part of the nervous system that directly perceives smells—reacted in real time to complex odors. They found that those nerve cells may play a larger and more complex role in interpreting smells than was previously understood.
“This is an elegant demonstration of the power of BRAIN Initiative technologies to provide new insights into how the brain decodes information to produce sensations, thoughts, and actions,” said Edmund Talley, Ph.D., program director, National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS), a part of NIH.
The SCAPE microscope was developed in the laboratory of Elizabeth M.C. Hillman, Ph.D., professor of biomedical engineering and radiology and principal investigator at Columbia’s Zuckerman Institute in New York City.
“SCAPE microscopy has been incredibly enabling for studies where large volumes need to be observed at once and in real time,” said Dr. Hillman. “Because the cells and tissues can be left intact and visualized at high speeds in three dimensions, we are able to explore many new questions that could not be studied previously.”
The olfactory epithelium is located deep within the nose and is made up of many thousands of nerve cells that each contain a single special receptor that reacts to a specific odor. Studies using individual, simple odors suggest that when we smell something, a specific combination of these nerve cells become activated, forming a code that is interpreted by the brain as that particular odor. In the past, researchers were only able to study a limited fraction of this area at any one time and the methods they used could damage the tissue, making it hard to draw definitive conclusions.
The olfactory epithelium proved to be an ideal target to study using SCAPE, because the nerve cells responsible for detecting odors are distributed somewhat randomly. This means that it is important to watch as many cells as possible to draw conclusions about their activity patterns.
Using SCAPE, the researchers who performed this study were able to measure thousands of olfactory nerve cells at once as they responded to combinations of different odors described as “almond,” “floral/jasmine,” and “citrus.” However, although they saw simple patterns predicted by the existing theory when they exposed the tissue to odors individually, when two or three odors were mixed together they saw a much more complex system of interactive nerve cell responses than expected.
“We expected the response to a mixture of odors to look a lot like the sum of responses to the original odors,” said Stuart Firestein, Ph.D., professor at Columbia University, New York City, and a senior author of the study. “Instead, we observed complex interactions where a second odor enhanced a neuron’s response to the first odor, or in other cases, inhibited a neuron’s response.”
These results suggest that the signals reaching the brain are distorted by these receptor interactions within the nose, altering the code for a mixture of odors into something perceptibly different from the sum of its parts. Given that almost all odors around us are complex mixtures, this mechanism might explain how we can distinguish between a huge variety of different smells, while also explaining why it can often be difficult to pick out a mixture’s individual ingredients.
“SCAPE provides a major advantage in that, because we can watch such a large area at one time, we can catch important events that happen rarely,” said Dr. Firestein. “This technique has opened the door for us to explore many additional questions in the olfactory field.”
Dr. Firestein also says he and others are now able to further study how complex odor combinations are encoded by the olfactory system and how those signals are eventually interpreted by the brain. The implications of this study also go beyond the current understanding of how the brain perceives odors, including a potential new way to screen drug candidates that affect the types of receptors at work in the olfactory system.
“This paper is transformative with respect to our understanding of how odor mixtures are encoded and highlights the remarkable complexity of odorant/receptor interactions,” said Susan Sullivan, Ph.D., program director, National Institute on Deafness and Other Communications Disorders (NIDCD), part of NIH and co-funder of this project.
In addition, several neurological disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease, and systemic diseases including COVID-19, often have loss of smell as an early symptom. A better understanding of the changes that cause this symptom could aid in an early detection system prior to the onset of more debilitating effects.
Because studies like this one involve collecting information on more than 10,000 cells over long periods of time, the amount of data gathered by the team was enormous. The team had to develop new analysis methods and even build their own computers to handle the computation.
“We are constantly improving and refining SCAPE, and intense interdisciplinary collaborations such as this one have been essential for guiding these innovations, further expanding what we can do with the technique,” said Dr. Hillman, whose team is working hard to share the SCAPE system with as many labs as possible, both through direct interactions, dissemination, and commercialization.
One of the goals of the BRAIN Initiative is to accelerate the development and application of innovative technologies for studying the nervous system. The SCAPE method was developed and refined, in part, thanks to funding through this initiative.
This project was funded by the NIH BRAIN Initiative (NS094296, NS108213), National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders (NIDCD; DC013553), National Cancer Institute (NCI; CA236554), the US Department of Defense, a Frimenich contract, the Simons Foundation Collaboration on the Global Brain, the Kavli Institute for Brain Science, and the National Science Foundation. SCAPE microscopy is licensed to Leica Microsystems.
For more information:
braininitiative.nih.gov
ninds.nih.gov
www.nidcd.nih.gov
Reference:
L Xu, et al. Widespread Receptor Driven Modulation in Peripheral Olfactory Coding. Science. April 10, 2020. DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz5390
###
NINDS is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD): The NIDCD supports and conducts research and research training on the normal and disordered processes of hearing, balance, taste, smell, voice, speech, and language and provides health information, based upon scientific discovery, to the public.
The NIH BRAIN Initiative® is managed by 10 institutes whose missions and current research portfolios complement the goals of the BRAIN Initiative: National Center for Complementary and Integrative Health, National Eye Institute, National Institute on Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development, National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, National Institute of Mental Health, and National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov.
