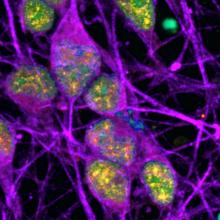
Neurons (labeled in purple) show signs of an active DNA repair process (labeled in yellow). The cells’ DNA itself is labeled in cyan (in this image, overlap between cyan and yellow appears green).
Image courtesy of Ward lab, NINDS
NIH labs collaborate to develop new methods for studying genome-wide DNA damage and repair
WHAT:
Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have discovered specific regions within the DNA of neurons that accumulate a certain type of damage (called single-strand breaks or SSBs). This accumulation of SSBs appears to be unique to neurons, and it challenges what is generally understood about the cause of DNA damage and its potential implications in neurodegenerative diseases.
Because neurons require considerable amounts of oxygen to function properly, they are exposed to high levels of free radicals—toxic compounds that can damage DNA within cells. Normally, this damage occurs randomly. However, in this study, damage within neurons was often found within specific regions of DNA called “enhancers” that control the activity of nearby genes.
Fully mature cells like neurons do not need all of their genes to be active at any one time. One way that cells can control gene activity involves the presence or absence of a chemical tag called a methyl group on a specific building block of DNA. Closer inspection of the neurons revealed that a significant number of SSBs occurred when methyl groups were removed, which typically makes that gene available to be activated.
An explanation proposed by the researchers is that the removal of the methyl group from DNA itself creates an SSB, and neurons have multiple repair mechanisms at the ready to repair that damage as soon as it occurs. This challenges the common wisdom that DNA damage is inherently a process to be prevented. Instead, at least in neurons, it is part of the normal process of switching genes on and off. Furthermore, it implies that defects in the repair process, not the DNA damage itself, can potentially lead to developmental or neurodegenerative diseases.
This study was made possible through the collaboration between two labs at the NIH: one run by Michael E. Ward, M.D., Ph.D. at the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) and the other by Andre Nussenzweig, Ph.D. at the National Cancer Institute (NCI). Dr. Nussenzweig developed a method for mapping DNA errors within the genome. This highly sensitive technique requires a considerable number of cells in order to work effectively, and Dr. Ward’s lab provided the expertise in generating a large population of neurons using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) derived from one human donor. Keith Caldecott, Ph.D. at the University of Sussex also provided his expertise in single strand break repair pathways.
The two labs are now looking more closely at the repair mechanisms involved in reversing neuronal SSBs and the potential connection to neuronal dysfunction and degeneration.
WHO:
Michael E. Ward, M.D., Ph.D., investigator, NINDS
Andre Nussenzweig, Ph.D., chief, Laboratory of Genomic Integrity, NCI
ARTICLE:
Wu W. et al. Neuronal enhancers are hot spots for DNA single-strand break repair. March 25, 2021. Nature. DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-03468-5
This study was supported by the NIH/NINDS/NCI Intramural Research Programs, an NIH Intramural FLEX Award, U.S. Department of Defense, Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Packard ALS Center, Alex’s Lemonade Stand Foundation, UK Medical Research Council, Cancer Research-UK, ERC Advanced Investigator Award, Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award, and an Ellison Medical Foundation Senior Scholar in Aging Award.
This media availability describes a basic research finding. Basic research increases our understanding of human behavior and biology, which is foundational to advancing new and better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat disease. Science is an unpredictable and incremental process — each research advance builds on past discoveries, often in unexpected ways. Most clinical advances would not be possible without the knowledge of fundamental basic research.
###
NINDS is the nation’s leading funder of research on the brain and nervous system. The mission of NINDS is to seek fundamental knowledge about the brain and nervous system and to use that knowledge to reduce the burden of neurological disease.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov.
