For the first time, scientists have recorded how our brains navigate physical space and keep track of others’ location. Researchers used a special backpack to wirelessly monitor the brain waves of epilepsy patients as each one walked around an empty room hunting for a hidden, two-foot spot.
Press Releases

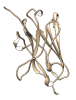
National Institutes of Health researchers have isolated a set of promising, tiny antibodies, or “nanobodies,” against SARS-CoV-2 that were produced by a llama named Cormac.
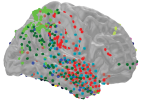
In a study involving epilepsy patients, National Institutes of Health scientists discovered how a set of high frequency brain waves may help us spot these kinds of differences between the past and the present.

The National Institutes of Health will provide support to institutions to recruit diverse groups or “cohorts” of early-stage research faculty and prepare them to thrive as NIH-funded researchers.

A study led by researchers at the National Institutes of Health has made a surprising connection between frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), two disorders of the nervous system, and the genetic mutation normally understood to cause Huntington’s disease.
In 2015, hundreds of children were born with brain deformities resulting from a global outbreak of Zika virus infections.
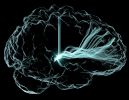
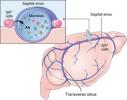
The membranes surrounding our brains are in a never-ending battle against deadly infections, as germs constantly try to elude watchful immune cells and sneak past a special protective barrier called the meninges.

A study published today in JAMA Network Open shows that children from poorer neighborhoods perform less well on a range of cognitive functions, such as verbal ability, reading skills, memory, and attention, and have smaller brain volumes in key cognitive regions compared to those from wealthier neighborhoods
In a National Institutes of Health (NIH)-funded study involving both mice and patients who are part of an NIH Clinical Center trial, researchers discovered that a gene, called PIEZO2, may be responsible for the powerful urge to urinate that we normally feel several times a day.
